Category : Light Hardwoods
Local Name : Terap
Family : Moraceae
|
Species
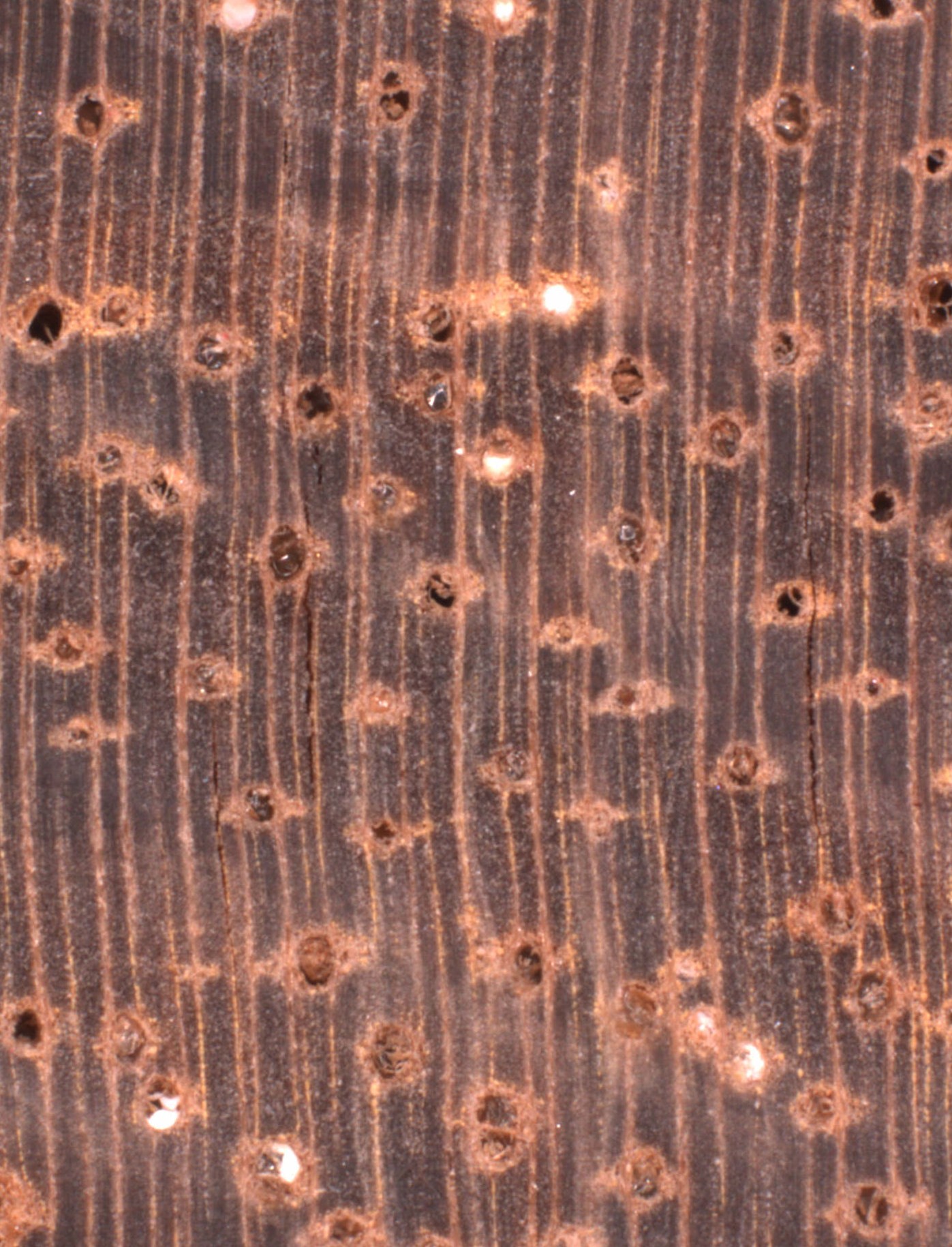
General Characteristics Sapwood generally not differentiated from heartwood; wood yellow-brown; some species yellow-brown with an orange tinge or orange-brown in which case sapwood is differentiated; planed surface moderately lustrous; stripe figure common; texture coarse but even; grain interlocked; soft to cut across grain; air dry density on an average 496 kg/m³ (31 lb/ft³); not durable.
Structure
Growth rings absent.
Other Features
Burning splinter test: Splinterburns to ash.
Uses The timber is suitable for light construction, strip flooring, core veneer in plywood manufacture, boxes, crates and wooden pallets.
|
